Emergency Intubation in ICUs: Etomidate or Ketamine – Weighing the Trade-offs
Time to read: Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI) Critically Ill Adults, Haemodynamic Instability, Emergency Intubation, Ketamine, Etomidate
Source: JAMA Network Open
Feature
Text

Early Restrictive vs Liberal Oxygen for Trauma Patients: The TRAUMOX2 Randomized Clinical Trial
Time to read:05:50.The study aimed to determine if limiting oxygen treatment during the first 8 hours post-injury would lead to better patient outcomes, such as lower mortality and fewer respiratory complications, within 30 days.
Source: JAMA
Text
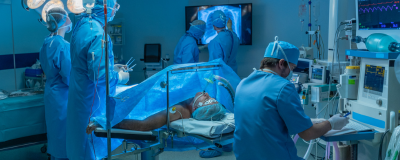
The role of perioperative sedative anesthetics in preventing postoperative delirium
Time to read: 07:16. Researchers of this study set out to investigate whether there is an effective sedative that can prevent postoperative delirium while also examining the safety of using sedatives during the perioperative period.
Source: BMC Cardiovascular Review
Text
Catecholamine concentration as a predictor of mortality in emergency surgical patients
Time to read: 07:49. This study aimed to determine whether the serum levels of epinephrine and norepinephrine at admission correlate with age and mortality in emergency surgical patients, including trauma and non-trauma patients.
Source: International Journal of Emergency Medicine
Text
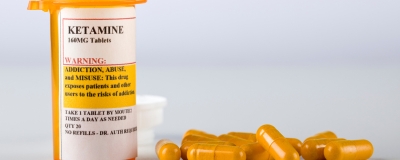
Assessment of Initial Depressive State and Pain Relief With Ketamine in Patients With Chronic Refractory Pain
imited research exists regarding the influence of pre-treatment of depressive symptoms on the relief experienced by patients with chronic pain when treated with ketamine. To address this gap, researchers Marion Voute, Céline Lambert, and Bruno Pereira et al. aimed to determine clinical pain trajectories experienced with repeated ketamine administration, exploring whether racemic (R/S) ketamine dose and/or pretreatment depressive and/or anxiety symptoms mediate pain relief.
Source: JAMA Open Networks
Text
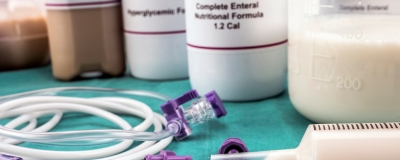
Nutrition therapy and critical illness: practical guidance for the ICU, post-ICU, and long-term convalescence phases
Improving care for intensive care survivors and their families requires collaboration between practitioners and researchers in both the inpatient and outpatient settings. Strategies and further research is required to address post-ICU QoL to improve outcomes for ICU survivors. According to the researchers of this review, van Zanten et al., optimal nutrition throughout hospitalization and recovery is one strategy that can be implemented to improve functional and QoL outcomes at a relatively low cost.
Source: Critical Care
Text
Interaction of acute heart failure and acute kidney injury on in-hospital mortality of critically ill patients with sepsis: A retrospective observational study
Preexisting heart failure (HF) in patients with sepsis is associated with a 75% death rate 1-year after discharge, whilst sepsis-induced AKI occurs in 40-50% of sepsis patients, resulting in a 6-fold increased mortality rate. While both, both AKI and AHF increase the risk of death in severe sepsis patients, it is unclear whether both act synergistically to increase the risk of in-hospital mortality.
Source: Plos One
Text
Testing a Novel Deliberate Practice Intervention to Improve Diagnostic Reasoning in Trauma Triage: A Pilot Randomized Clinical Trial
Undertriage due to diagnostic errors remains common despite efforts to standardize triage practices. Clinicians must evaluate and stabilize a patient's injuries and determine whether to transfer to a trauma centre. A timely and accurate explanation of injuries presented at the non-trauma centre shortens the duration of pain and reduces mortality by 10-25%. Goal-oriented training with a coach who provides immediate, personalized performance feedback has not previously been used in trauma triage to improve diagnostic reasoning. This study aims to test this theory.
Source: JAMA
Text
Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation for cardiac arrest: An updated systematic review
In 2018, the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) systematically reviews existing literature to address these issues. At the time of its review, no randomised trials were available & what information was available showed weak evidence to support its use. These factors, coupled with the expense of the procedure, resulted in a weak recommendation in the cardiac guidelines. This study by Mathias et al., set out to update the ILCOR review based on new information studies published between 2018 and 2022.
Source: Resuscitation
Text



